CCTV stands for “closed-circuit television.” A system of video cameras that are used to transmit signals to a specific, limited set of monitors or recording devices. The purpose of CCTV is usually to monitor and record activity in a specific area, such as a building, a public space, or a transportation hub. CCTV systems can be used for a variety of purposes, such as crime prevention, traffic monitoring, crowd control, and workplace safety security,& surveillance of businesses, government buildings, public spaces, and private residences.
Additionally
- CTV cameras can be either analog or digital. Analog cameras transmit video signals over coaxial cables, while digital cameras transmit video signals over an IP network.
- CCTV systems can vary in complexity from a single camera connected to a monitor, to a network of cameras connected to multiple monitors and recording devices.
- CCTV footage can be recorded onto hard drives of digital video recorders (DVRs), or network video recorders (NVRs). The footage can be stored for a specified amount of time and can be accessed later for review or analysis.
- CCTV systems can include additional features such as motion detection, facial recognition, and license plate recognition & other Ai Features, These features can be used to trigger alarms or alerts, or to automatically track individuals or vehicles.
CCTV Terminology
CCTV camera:
A device that captures and transmits video images for surveillance or security purposes. CCTV cameras come in many different types and styles, with varying features and capabilities.Common types of CCTV cameras:
Dome Camera:
A camera that is housed in a dome-shaped enclosure, typically mounted on a ceiling. Dome cameras are discreet and can provide a wide field of view.
BulletCamera
A camera that is housed in a cylindrical enclosure, typically mounted on a wall. Bullet cameras are more visible than dome cameras but can be more durable and weather-resistant.
PTZ Camera: A pan-tilt-zoom camera that can be remotely controlled to adjust its field of view, zoom in on specific areas, and track moving objects.
Box Camera
A box camera is a type of CCTV camera that is housed in enclosure. The enclosure is typically made of metal or plastic and is designed to protect the camera and its internal components from damage.

Thermal Camera
A camera that detects heat signatures to produce images in low-light or no-light conditions.
360-Degree Camera
A camera that captures a panoramic view of its surroundings, often used for surveillance in large areas such as warehouses or parking lots.FishEye Camera is the best Example.


Wireless Camera: A camera that transmits video footage wirelessly to a monitor or recorder.
Video Compression

the process of reducing the size video file while retaining its quality. Video compression is necessary because video files are typically very large due to the large number of pixels and frames that make up the video. Compression techniques are used to reduce the amount of data for faster transmission without significantly affecting the quality of the video & less storage hardware requirements .lossless and lossy are the two type of compression
• Lossless algorithms reduce the size of a video file without losing any information. This type of compression is often used for professional video editing applications where preserving the original quality of the video is important.
• Lossy compression algorithms, on the other hand, sacrifice some information to achieve higher levels of compression. This type of compression is commonly used for video distribution over the internet, where smaller file sizes are more important than maintaining the highest possible level of quality.
Some common video compression standards :
H.264
H.264, also known as MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC (Advanced Video Coding), is a widely used video compression standard
H.264 is known for its high compression efficiency, which means it can reduce the size of video files without significantly degrading the quality of the video. This makes it well-suited for a wide range of applications, from streaming video over the internet to Blu-ray discs and high-definition television broadcasts.
H.264 also supports a range of video resolutions and frame rates, allowing CCTV systems to capture high-quality video of varying levels of detail and motion. H.264 also supports various advanced features, such as motion detection and digital zoom, which are useful for surveillance applications.
H.265
H.265, also known as High-Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), is a video compression standard that was developed to succeed the widely used H.264/MPEG-4 AVC (Advanced Video Coding) standard.H.265 offers improved compression efficiency compared to H.264, which means that it can deliver the same video quality at a lower bit rate or higher quality at the same bit rate.
Field of View
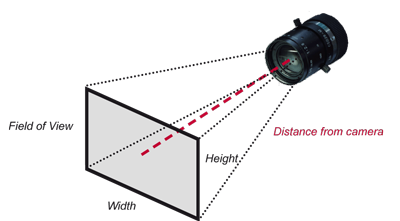
The field of view of a CCTV camera is determined by the camera’s focal length, sensor size, and placement.
The field of view of a CCTV camera can be adjusted by changing the camera’s lens or by adjusting its position. A camera with a fixed lens will have a fixed field of view, while a camera with a zoom lens can adjust its field of view by changing the focal length of the lens
CCTV cameras are often used for security and surveillance purposes, and the field of view is an important factor to consider when designing a CCTV system. A camera with a wide field of view can monitor a larger area, but may not capture as much detail as a camera with a narrower field of view. On the other hand, a camera with a narrower field of view can capture more detail, but may not be able to monitor as large an area.
Resolution:
Resolution refers to the level of detail that can be captured by a camera. It is typically measured in pixels and represents the number of pixels that make up the image captured by the camera. The higher the resolution, the more detail can be captured.
CCTV cameras are available in a range of resolutions, from standard definition (SD) to high definition (HD) and even ultra-high definition (UHD, also known as 4K). The most common resolutions used in CCTV are:
SD (standard definition): 720×480 pixels
HD (high definition): 1920×1080 pixels
UHD (ultra-high definition): 3840×2160 pixels
Higher resolution cameras can capture more detail, making them ideal for applications where high levels of detail are important, such as facial recognition or license plate reading. However, higher resolution cameras also require more storage space and processing power, so it’s important to balance the need for detail with practical considerations such as storage capacity and processing power.
pixels that a camera can capture is measured in terms of horizontal and vertical pixels, such as 1080p (1920×1080) or 4K (3840×2160).

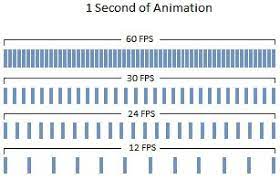
Frame rate
Frame rate refers to the number of individual images, or frames, captured by the camera per second. It is typically measured in frames per second (fps) and represents the number of still images that are captured in the span of one second.
The frame rate is an important factor to consider when designing a CCTV system, as it can impact the smoothness and clarity of the video footage. Higher frame rate produce smoother picture and more detailed footage, while a lower frame rate canprovide a choppy or blurry footage.
The most common frame rates used in CCTV are:
30 fps: This is the maximum frame rate for most CCTV cameras. It provides smooth and detailed footage, but requires more storage space and processing power.
15 fps: This is a lower frame rate that can still provide reasonably smooth footage, but requires less storage space and processing power.
10 fps or lower: This frame rate is typically used for applications where storage space and processing power are limited, such as remote monitoring over a low-bandwidth network.
Bitrate
Bitrate refers to the amount of data that is transmitted by the camera per second. It is typically measured in bits per second (bps) or kilobits per second (kbps) and represents the amount of data that is required to transmit the video footage from the camera to the recording device or monitor.
The bitrate is an important factor to consider when designing a CCTV system, as it can impact the quality of the video footage and the amount of storage space required to store the footage. A higher bitrate can provide higher quality footage with more detail and less compression artifacts, but requires more storage space and higher network bandwidth. A lower bitrate can reduce the storage space requirements and network bandwidth, but may result in lower quality footage with more compression artifacts.
The most common bitrates used in CCTV are:
1 Mbps or lower: This bitrate is typically used for applications where storage space and network bandwidth are limited, such as remote monitoring over a low-bandwidth network.
2-4 Mbps: This bitrate is typically used for standard definition (SD) cameras.
10-20 Mbps: This bitrate is typically used for high definition (HD) cameras.

Wide dynamic range (WDR)
Wide dynamic range (WDR) is a feature that is available on many CCTV cameras. It is designed to help the camera capture clear and detailed images in challenging lighting conditions, such as areas with high contrast between light and dark areas.
In a typical scene, there may be areas that are brightly lit, such as a window or a doorway, as well as areas that are in shadow, such as a corner of a room

WDR uses advanced image processing techniques to capture detail in both the bright and dark areas of the scene, resulting in a more balanced and detailed image. It works by capturing multiple images of the scene at different exposure levels and combining them into a single image that preserves detail in both the bright and dark areas.
There are two types of WDR: digital WDR and true WDR. Digital WDR is a software-based solution that uses image processing techniques to adjust the exposure of different parts of the image, while true WDR is a hardware-based solution that uses specialized sensors to capture multiple exposures simultaneously.
Infrared (IR)
Infrared (IR) is a technology that is commonly used in CCTV cameras to capture images in low light or no light conditions. IR light is invisible to the human eye but can be detected by IR sensors in CCTV cameras.
In an IR CCTV camera, an array of IR LEDs (light-emitting diodes) is used to illuminate the area being monitored. The camera’s IR sensor detects the reflected IR light and captures an image, even in complete darkness. This allows the camera to monitor areas where there is no ambient light, such as outdoor areas at night or indoor areas with no windows or artificial lighting.
IR CCTV cameras are available in a range of configurations, including bullet cameras, dome cameras, and PTZ (pan-tilt-zoom) cameras.
CBR (Constant bitrate)
Constant bitrate (CBR) is a method of video compression that is used in many CCTV systems. It involves encoding the video footage at a fixed bitrate, meaning that the amount of data used to represent each frame of the video is the same.
In CBR, the bitrate is set at a constant level throughout the video, regardless of the complexity or motion of the scene being captured. This can result in a more predictable and consistent level of video quality, as there are no fluctuations in the amount of data used to represent each frame.
CBR is often used in CCTV systems where the available bandwidth or storage space is limited, as it can help to ensure that the video footage remains within a specific size or quality range

Variable bitrate (VBR)
Variable bitrate (VBR) is a method of video compression that is used in many CCTV systems. Unlike constant bitrate (CBR), which encodes video at a fixed bitrate, VBR adjusts the bitrate dynamically based on the complexity of the scene being captured.
In VBR, the bitrate is allowed to vary based on the level of motion and detail in each frame of the video. The video encoder uses a higher bitrate to capture complex or high-motion scenes and a lower bitrate to capture simpler or low-motion scenes. This can result in more efficient use of bandwidth and storage space, as the video encoder is able to allocate more data to the frames that require it most.
VBR is often used in CCTV systems where the available bandwidth or storage space is limited, as it can help to ensure that the video footage remains within a specific size or quality range while still capturing the complexity and detail of the scene being recorded. It is also commonly used in applications where the level of motion or detail in the scene being recorded varies widely, such as in traffic monitoring or surveillance of public spaces.
Digital noise reduction (DNR)

Digital noise reduction (DNR) is a feature that is commonly used in CCTV cameras to reduce the amount of noise or graininess in the video footage. Noise can be caused by a variety of factors, including low light levels, high ISO settings, and compression artifacts.
DNR works by analyzing the video footage and removing or reducing the noise in each frame. This can result in a cleaner, smoother image with less visible noise or grain. DNR is typically achieved through software-based algorithms that are applied to the video footage in real-time or during post-processing.
There are different types of DNR methods that can be used, including 2D and 3D DNR. 2D DNR analyzes each frame of the video footage individually, while 3D DNR analyzes multiple frames of the video footage to better identify and remove noise.
DNR can be a useful feature in CCTV systems, as it can help to improve the quality and clarity of the video footage.
NTSC (National Television System Committee,)
In the context of CCTV (closed-circuit television), NTSC stands for National Television System Committee, which refers to a video standard used for analogue video surveillance systems in North America and some other countries.
CCTV cameras that use the NTSC standard typically produce a video signal with approximately 720 x 480 pixels, 30 frames per second (fps) resolution with an aspect ratio of 4:3 Analog CCTV systems that use the NTSC standard typically use coaxial cable to transmit video signals between cameras, recorders, and monitors. Measured in TVL(TV Line
PAL (Phase Alternating Line. )
in the context of CCTV (closed-circuit television), PAL stands for Phase Alternating Line. It is a video standard used in many countries
Like NTSC, PAL is an analogue video standard that specifies the number of lines, frame rate, and other parameters for video signals. PAL video has a resolution of 625 lines and a frame rate of 25 frames per second, with an aspect ratio of 4:3. PAL also uses a different colour encoding system than NTSC, which affects the way colours are displayed in the video.
CCTV cameras and recorders that use the PAL standard are designed to produce video signals that conform to this standard. This ensures that the video can be displayed on PAL-compatible monitors.
Auto Iris

In CCTV (closed-circuit television), an auto iris is a feature of a camera lens that automatically adjusts the size of the lens aperture to maintain a consistent level of light on the camera’s image sensor.
An auto iris lens can adjust the aperture to allow more or less light to enter the camera, depending on the brightness of the scene. For example, in bright daylight conditions, the lens aperture would be smaller to prevent overexposure of the image. In low-light conditions, the lens aperture would be larger to allow more light to enter the camera and produce a brighter image.
Types of auto iris lenses:
DC-controlled
DC-controlled auto iris lenses use a separate wire to control the iris opening
video-controlled.
Video-controlled auto iris lenses use a signal embedded in the video signal to control the iris opening.
Auto iris lenses are commonly used in outdoor locations where lighting conditions can change frequently, such as parking lots, building entrances, and other areas where natural light is present. They can also be used in indoor locations where lighting conditions can change, such as lobbies, stairwells, and other areas with windows or skylights.
The auto iris feature can improve the overall image quality and clarity of CCTV video by ensuring that the camera maintains a consistent level of light on the image sensor.
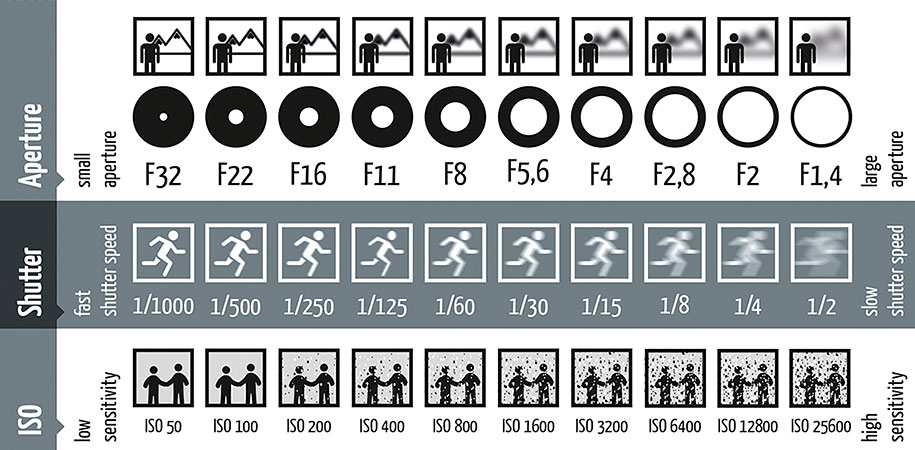
 Aperture
Aperture
Aperture refers to the size of the opening in the camera lens through which light passes to the camera’s image sensor. The aperture size is measured in f-stops, which represent the ratio of the lens’s focal length to the diameter of the aperture.
A larger aperture (indicated by a smaller f-stop number) allows more light to enter the camera, which can be useful in low-light conditions to produce a brighter image. However, a larger aperture also reduces the depth of field, which means that objects in the foreground or background may be out of focus.
a smaller aperture (indicated by a larger f-stop number) allows less light to enter the camera, which can be useful in bright daylight conditions or when a larger depth of field is desired. However, a smaller aperture also reduces the amount of light that reaches the camera’s image sensor, which can result in a darker image.
In CCTV cameras, the aperture size can be adjusted manually or automatically. Manual adjustment is typically done using a ring on the camera lens, while automatic adjustment can be done using an auto iris feature that adjusts the aperture size based on the lighting conditions in the scene.
The aperture size is an important factor in determining the overall image quality and clarity of CCTV video. A properly adjusted aperture can help ensure that the image is neither too bright nor too dark and that objects in the scene are in focus with an appropriate depth of field.
 BLC(Back Light Compensation)
BLC(Back Light Compensation)
In CCTV (closed-circuit television), Back Light Compensation (BLC) is a feature that allows a camera to compensate for bright light sources in a scene that can cause objects in the foreground to appear dark or silhouetted.
When a bright light source such as the sun or a bright lamp is behind an object in the scene, it can cause the object to be underexposed and appear dark in the resulting image. BLC compensates for this by adjusting the exposure level of the camera to improve the visibility of the foreground object.
BLC works by measuring the overall brightness level of the scene and adjusting the exposure level of the camera to compensate for the bright light source. This can be done manually or automatically, depending on the camera’s settings.
Some CCTV cameras also include a feature called Wide Dynamic Range (WDR), which is a more advanced version of BLC. WDR can compensate for both bright and dark areas of a scene, allowing objects in both the foreground and background to be visible in the resulting image.
BLC and WDR are particularly useful in outdoor surveillance applications where bright sunlight or other light sources can cause objects in the foreground to be underexposed. They can also be useful in indoor applications where there are bright windows or other light sources in the background of the scene.
Focal Length

In CCTV (closed-circuit television), focal length refers to the distance between the camera’s lens and the image sensor, measured in millimetres. The focal length determines the field of view and magnification of the camera’s image.
A shorter focal length lens produces a wider field of view, allowing the camera to capture more of the scene. This can be useful in applications where a broad overview of a large area is required, such as in a parking lot or warehouse. However, a shorter focal length also produces less magnification, which can make objects in the scene appear smaller.
Conversely, a longer focal length lens produces a narrower field of view, allowing the camera to focus on a smaller area with greater magnification. This can be useful in applications where detailed images of a specific area or object are required, such as in a bank or retail store. However, a longer focal length lens also produces a smaller field of view, making it more difficult to capture a broad overview of a large area.
CCTV cameras with adjustable focal length lenses are available,


 Aperture
Aperture BLC(Back Light Compensation)
BLC(Back Light Compensation)