QNAP 12-Bay 2U NAS,
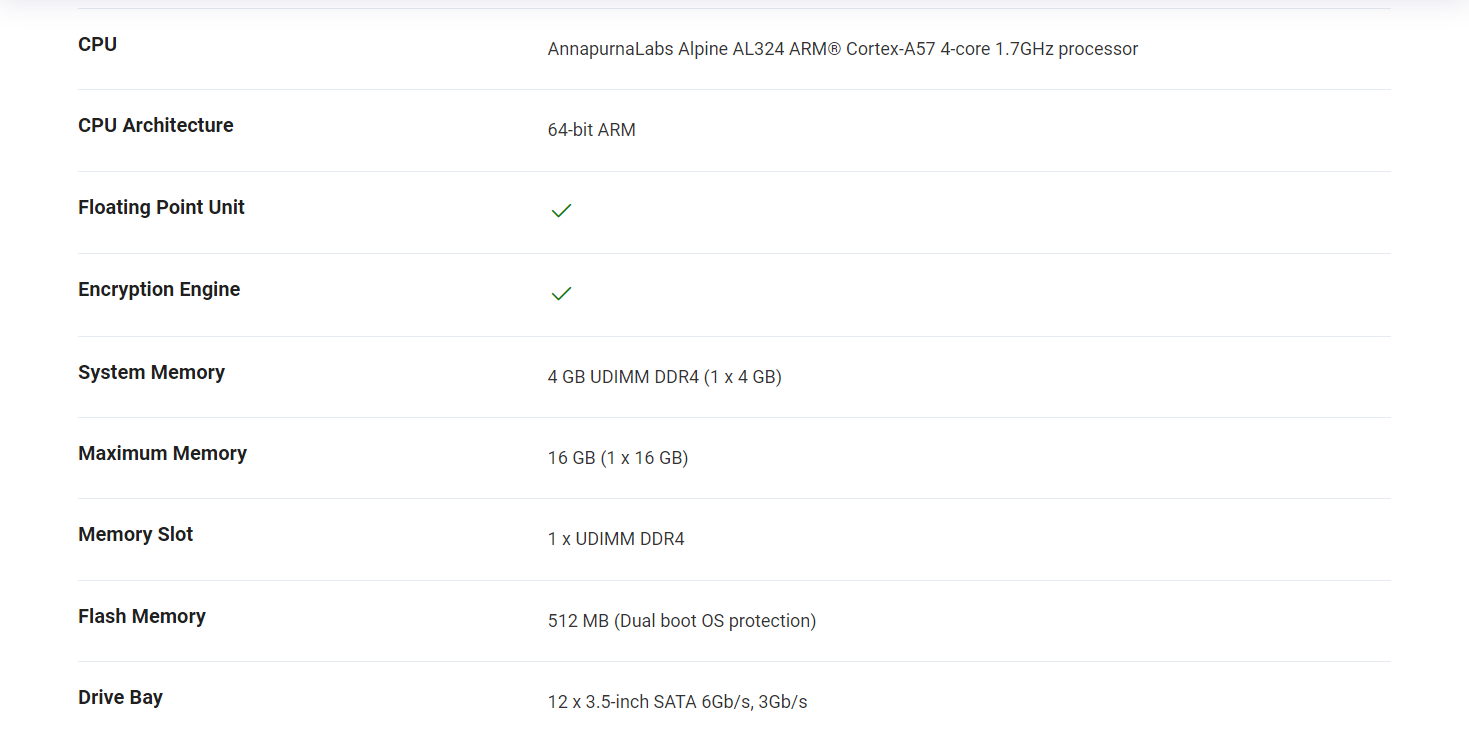
A NAS is a specialized storage device that is connected to a network and allows multiple users or devices to access and share data over a network. The “12-Bay” indicates that this particular NAS model has 12 drive bays, which means it can accommodate up to 12 hard drives or solid-state drives (SSDs) for storage purposes. The “2U” designation refers to the form factor of the NAS, indicating that it is designed to fit within a 2U rack space.
QNAP is a well-known manufacturer of NAS devices and offers a wide range of models with various features and capacities to meet different storage needs. The 12-bay configuration provides ample storage capacity for businesses, organizations, or individuals with significant data storage requirements.
Some key features commonly found in QNAP NAS devices include:
RAID Support: QNAP NAS devices support various RAID configurations, RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10.
Scalability: Many QNAP NAS models, including the 12-bay variants, allow for easy expansion of storage capacity. This can be achieved by adding additional drives to the available drive bays or by connecting expansion units to the NAS.
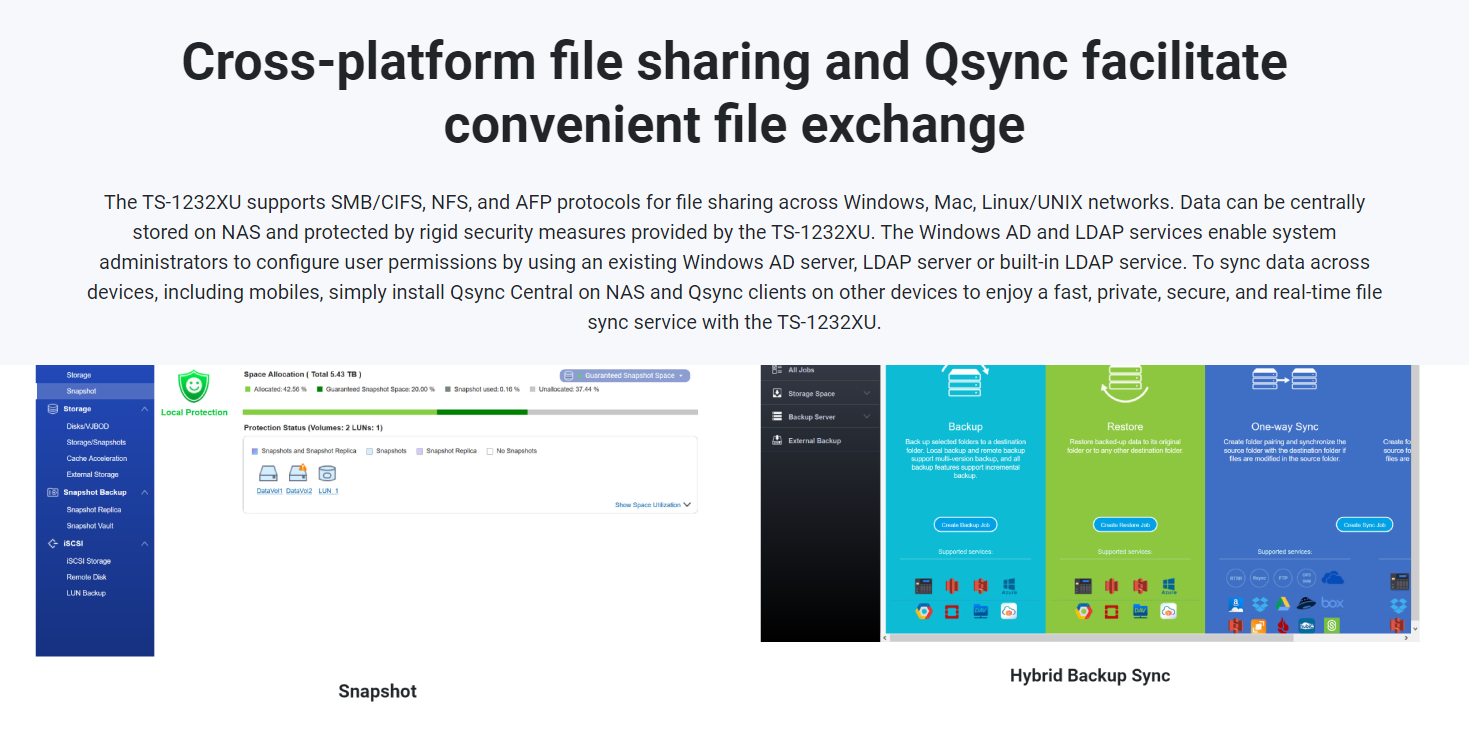
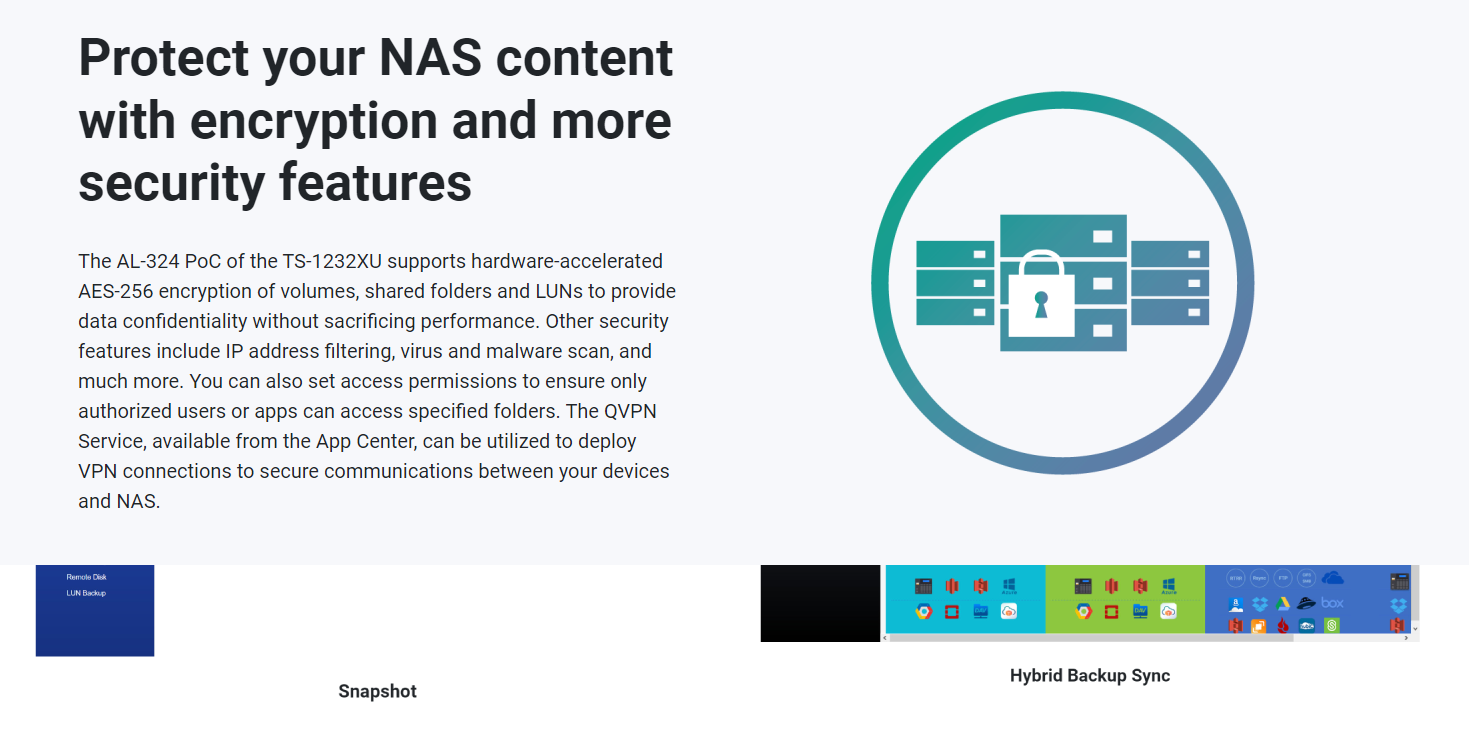
Data Protection: QNAP NAS devices typically provide features for data protection, such as regular backups, snapshot functionality, and data encryption. These features help safeguard data against accidental loss, hardware failures, or unauthorized access.
Network Services: QNAP NAS devices often come with built-in network services, such as file-sharing protocols (e.g., SMB, NFS), FTP, web servers, and media streaming capabilities. These services enable users to access and share files, host websites, or stream media content across the network.
Application Ecosystem: QNAP NAS devices support a wide range of applications that can be installed directly on the device. These applications include productivity tools, multimedia applications, surveillance software, virtualization platforms, and more. The application ecosystem enhances the functionality and versatility of the NAS device.








Check the Price 
FAQ
- What is NAS storage used for?
NAS (Network-Attached Storage) is a type of storage device or system that is connected to a network and provides file-level data storage and access to multiple clients or users. It is designed to facilitate centralized data storage, file sharing, and data backup in homes, small businesses, and enterprise environments
What is SAN vs NAS storage?
SAN (Storage Area Network) and NAS (Network-Attached Storage) are two different storage architectures used in enterprise environments. While they both serve the purpose of providing storage solutions, there are some key differences between SAN and NAS:
SAN:
Architecture: SAN is a high-speed network dedicated to storage and operates at the block level. It uses Fiber Channel or iSCSI protocols to connect servers and storage devices.
Block-Level Access: SAN provides block-level access to storage resources. It presents storage volumes as block devices directly to servers, and the file system and data management are handled by the server’s operating system.
Performance: SAN typically offers higher performance and lower latency than NAS due to its direct block-level access. It is suitable for applications that require high-speed access to storage, such as databases or virtualization environments.
Centralized Storage: SAN consolidates storage resources into a centralized pool that can be shared by multiple servers. This allows for efficient storage management and resource utilization.
Complex Configuration: Setting up and managing a SAN can be more complex than NAS, requiring specialized knowledge and expertise. It often involves configuring switches, zoning, and configuring storage arrays.
NAS:
Architecture: NAS is a storage system that connects to the network and operates at the file level. It uses standard network protocols such as Ethernet and TCP/IP.
File-Level Access: NAS provides file-level access to storage resources. It has its own operating system and file system, allowing it to manage file operations independently. Clients access files over the network using protocols like NFS (Network File System) or SMB/CIFS (Server Message Block/Common Internet File System).
Simplicity and Ease of Use: NAS is generally easier to set up and manage compared to SAN. It has a user-friendly interface and does not require specialized knowledge. Configuration and administration tasks are typically performed through a web-based interface.
File Sharing and Collaboration: NAS is well-suited for file sharing and collaboration scenarios. It allows multiple users to access and share files simultaneously, making it ideal for environments where data sharing and collaboration are important.
Cost-Effectiveness: NAS solutions are often more cost-effective than SAN, especially for smaller-scale deployments. They use standard Ethernet infrastructure and can leverage existing network resources.
Which is faster SAN or NAS?
SAN (Storage Area Network) tends to provide faster performance compared to NAS (Network-Attached Storage), SANs typically use high-speed protocols like Fibre Channel or iSCSI, which are optimized for fast, dedicated storage connectivity. SANs can also take advantage of features such as multi-pathing and hardware-level RAID
Which NAS is the best?
Synology
QNAP, Asustor
Western Digital

