Gas exposure can be fatal. Leaks of combustible gases can cause explosions, while toxic gases like carbon monoxide can be deadly. It’s important to be aware of these risks and take the necessary precautions to stay safe. A gas detector system is a device or a group of devices that are designed to detect specific gases in the air commonly used in industries, commercial spaces, and even homes, to ensure safety and prevent potential dangers. There are two main types of gas detectors:
Fixed gas detectors
permanently installed in specific locations, such as factories, plants, or confined spaces. They continuously monitor the air quality in those areas.
Portable gas detectors
Handheld devices that individuals can carry around to detect gases in different places.
Control Panel
The control panel is the central unit of a fixed gas detection system. It receives signals from the gas sensors, displays gas concentrations, and provides audible and visual alarms in case of gas leaks or hazardous conditions.
Alarms and Indicators
Gas detectors have audible and visual alarms to alert individuals when gas concentrations exceed pre-set thresholds. These alarms can be in the form of sirens, strobe lights, or digital displays. Some systems also offer remote alarms connected to a building’s fire alarm system for wider notification.
Data Logging and Communication
Many modern gas detector systems include data logging capabilities, allowing them to record gas concentrations over time. This data can be used for analysis, compliance reporting, and identifying trends. Additionally, some systems have built-in communication options like Ethernet, Wi-Fi, or Modbus, enabling remote monitoring and integration with other safety systems.
Power Supply and Backup
Gas detectors require a reliable power supply. Fixed systems are typically hardwired to the electrical grid, while portable devices may rely on batteries. Some systems also incorporate battery backup or an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to ensure continuous operation during power outages.
Calibration and Maintenance
Regular calibration and maintenance of the gas detector system are essential to ensure accurate and reliable gas detection. Calibration involves comparing the sensor’s readings to a known concentration of gas to adjust its sensitivity. Maintenance may include sensor replacement, filter cleaning, and general system checks.
Where do I install gas detectors?
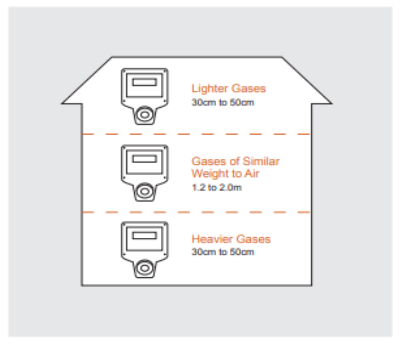
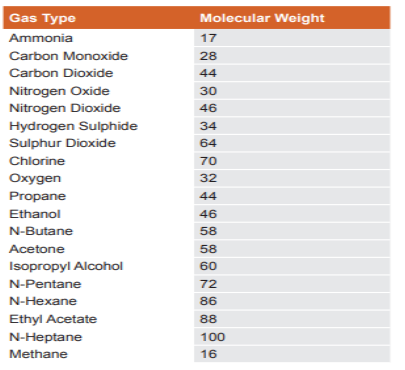
The ideal location to install a gas detector depends on the targeted gas. As a general guideline, for gases that are lighter than air,
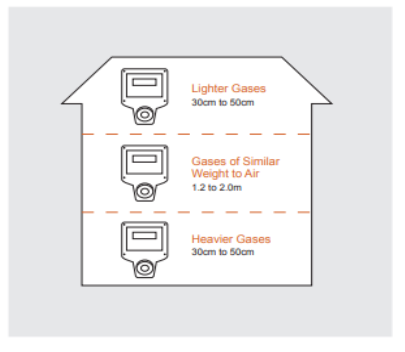
Installing a detector 30–50 cm from the ceiling is recommended. For gases heavier than air, the detector should be installed 30–50 cm from the floor. If the gas being detected has a similar weight to air, it is advisable to install the gas detector at a height close to the head (approximately 1.2 to 2.0m). Following these placement recommendations can help optimise the effectiveness of the gas sense detector in detecting and alerting potential gas hazards. The coverage of these detectors will depend on the
target gas, and the airflow conditions in the area to be protected. The typical coverage is 50 m2. If the gas detector is being installed to monitor a specific area, then the detector should be located approximately 1.5 metres away from that point.
How do I place the gas detectors in their best location?
When choosing the best place to install the detector, consider all other environmental factors in that area, such as:
Ventilation or Air Conditioning Vents: Do not place a detector where forced air flow will prevent gas from entering the detector.
Open Windows: Airflow through an open window can prevent gas from entering the detector.
 Dust and debris: avoid placing the detector where a constant generation of debris could block the filter, preventing gas from entering the sensor chamber.
Dust and debris: avoid placing the detector where a constant generation of debris could block the filter, preventing gas from entering the sensor chamber.
Maintenance access: critical detectors should be checked regularly, and the sensor will need to be
replaced every 3-5 years. Do not fit in an inaccessible location.
Ceiling beams: if a lighter-than-air gas is to be detected, large ceiling beams can affect coverage. requiring a detector between each beam.
When should I test gas detectors?
The frequency of gas detector testing should be determined based on a thorough risk analysis of the area being protected. If the potential consequences of a gas leak are relatively minor, it may be acceptable to perform checks every 6 months or even once a year. However, if the consequences of a leak could be severe, it is considered good practice to regularly check the calibration of the gas detector. This ensures that the detector accurately detects gas levels and maintains effectiveness in detecting and alerting potential hazards. By conducting regular testing and calibration, the gas detector can be relied upon to provide timely and accurate warnings, helping to minimise risks and ensure the safety of the protected area. To properly test a gas detector for toxic gases, it is generally recommended to use the target gas at around 50% of the detector’s rating. This helps ensure accurate calibration and reliable detection.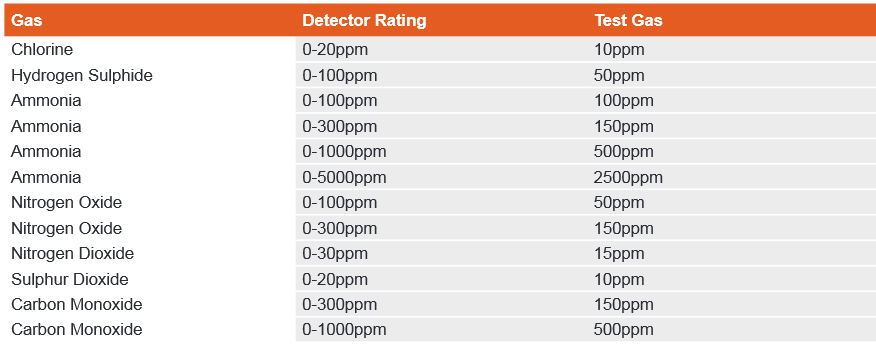
You have the flexibility to test gas detectors at lower concentrations if needed, depending on the site requirements. When testing combustible gas detectors, it is important to use methane gas for methane detectors. A concentration of 2.5% volume of methane will correspond to 50% of the Lower Explosive Limit (LEL). For other combustible gases, you can either test them with the exact gas or use propane as a substitute. If using propane, a cylinder containing 50% LEL propane will provide accurate readings.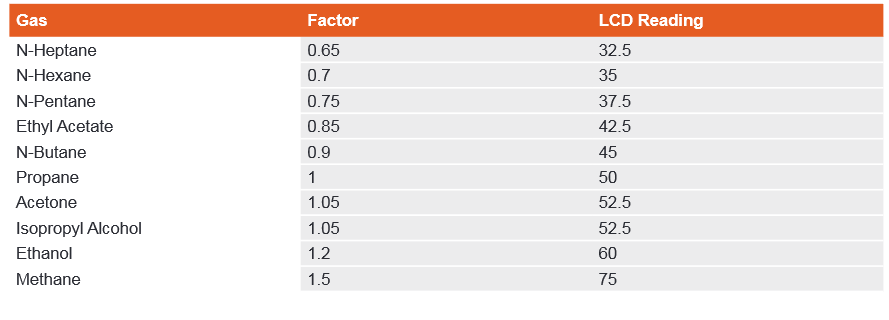
How do I connect gas detectors to the panel?
Connecting gas detectors to a panel depends on the type of gas detection system you are using.
Here’s a short step-by-step guide to connecting gas detectors to a panel: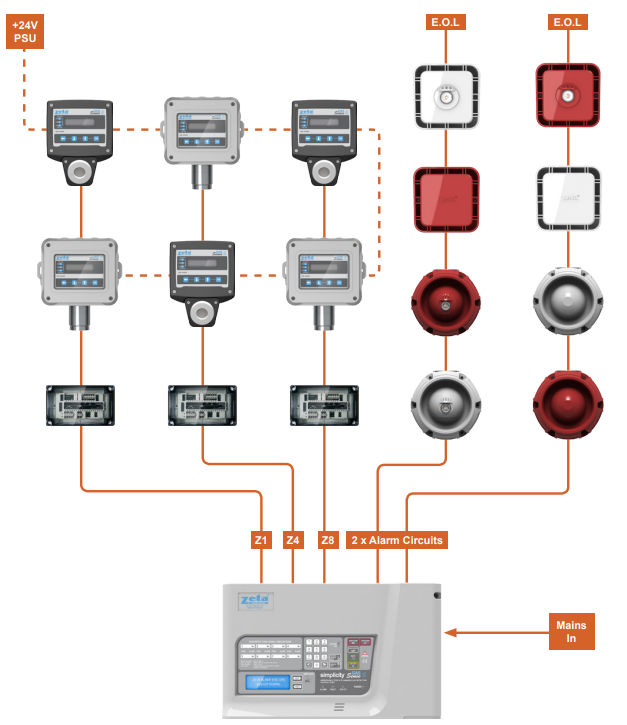
- Choose the appropriate gas detectors based on the gases you want to detect.
- Review the manufacturer’s instructions to understand the wiring requirements, including communication protocol, wiring connections, and power supply.
- Provide the necessary power supply to the gas detectors according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Connect the communication wires between the gas detectors and the panel based on the recommended wiring connections for the communication protocol used.
What is the NFPA standard for gas detection?
The NFPA standard for gas detection is NFPA 72: National Fire Alarm and Signaling Code. It provides guidelines for the design, installation, testing, and maintenance of gas detection systems as part of fire alarm and signalling systems. It covers aspects such as detector placement, wiring, communication, testing, and integration with fire alarm systems. It’s important to consult the latest edition of the standard and any local codes for specific requirements in your jurisdiction.
What is NFPA 72 standards? Does NFPA 72 cover gas detection?
NFPA 72 covers a wide range of topics related to fire alarms and signalling systems. It provides guidelines for the design, installation, testing, operation, and maintenance of fire alarm systems and gas detection systems.

 Dust and debris: avoid placing the detector where a constant generation of debris could block the filter, preventing gas from entering the sensor chamber.
Dust and debris: avoid placing the detector where a constant generation of debris could block the filter, preventing gas from entering the sensor chamber.
